Diabetic retinopathy is a complication that occurs in the majority of patients with diabetes, where damage to the blood vessels due to high blood sugar leads to circulatory disorders in the peripheral vessels of the retina. In the early stages, symptoms may not be noticeable, making it difficult to detect the disease. However, if left untreated or if the appropriate treatment is delayed, it can potentially lead to blindness.
Classification and Symptoms
Diabetic retinopathy is classified into proliferative and nonproliferative based on the presence or absence of neovascularization that grows through the boundary membrane of the retina.
Nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy is the most common, accounting for approximately 80% of patients with diabetic retinopathy. It can lead to additional complications such as microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, and hard exudates. In severe cases, diabetic macular edema may occur, adversely affecting vision.
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy involves the formation of new blood vessels due to inadequate blood supply. Abnormally formed vessels are prone to rupture, leading to serious eye conditions such as vitreous hemorrhage, anterior segment hemorrhage, fibroproliferation, and tractional retinal detachment (TRD).
These complications can potentially result in blindness.
-
Blurred vision
-
Difficulty in daily activities,
especially at night -
Seeing flashes of light or photopsia
when blinking -
Experiencing floaters, which are drifting threads in the field of vision
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is conducted through fundus photography, fundus autofluorescence, fluorescein angiography, and optical coherence tomography
The One Seoul Eye Clinic has introduced the Ultra-widefield Retinal Imaging Device, allowing for a comprehensive view of the entire retina, as well as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), which is a non-invasive and high-resolution imaging technique, enabling precise diagnosis and treatment.
-
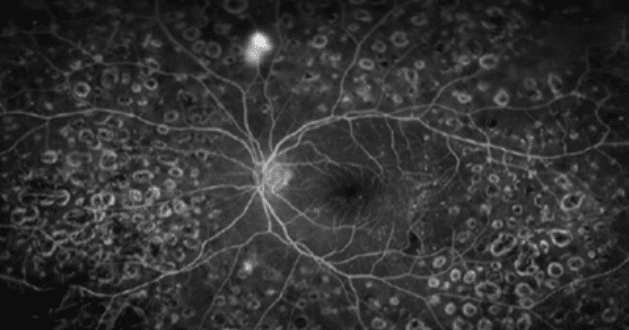
Neovascularization Detected by Fluorescein Angiography (FAG)
-
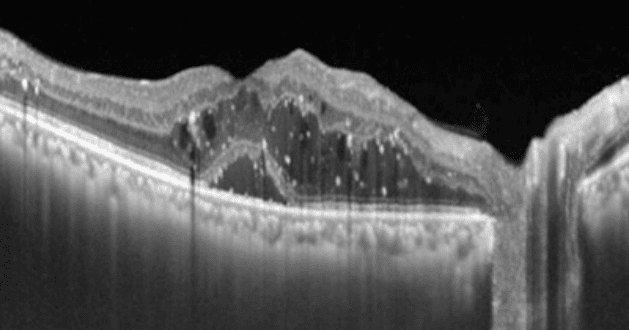
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) Detected by Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Treatment
For individuals with diabetes as an underlying condition, it is advisable to undergo eye examinations at least once a year. Strict management of blood sugar levels, blood pressure, cholesterol, and kidney function is crucial.
In the case of the development of diabetic retinopathy, especially severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy, examinations every 2-4 months are necessary.
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, efforts to control blood pressure, blood sugar level, and fat in the blood are essential, along with periodic monitoring of progress.
In advanced cases, treatment options such as antibody injections, laser treatments, and surgical treatments can be considered based on the onset and progression.
Antibody injection, which prevents the formation of new blood vessels, can delay the onset of the disease and potentially lead to vision improvement.
However, if blood vessels are already damaged, panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) using laser on the peripheral retina can suppress the formation of new blood vessels. In cases where new blood vessels proliferate into the iris, vitrectomy can be performed to remove the cloudy vitreous and new blood vessels.
Combining ophthalmic and internal medicine treatments during the treatment of diabetic retinopathy can enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment.
-
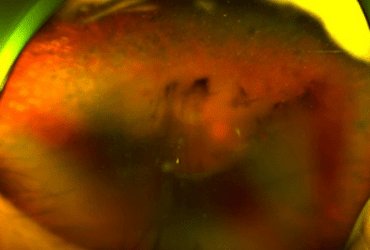
Before Treatment
Vitreous Hemorrhage
- Vitrectomy
-
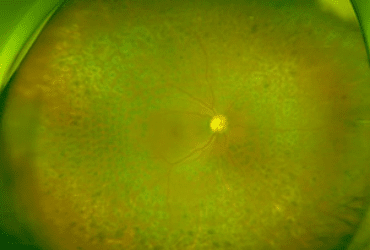
After Treatment
No Vitreous Hemorrhage
The One Seoul Eye Clinic considers the clinical characteristics and pathological patterns of diabetic retinopathy, offering various intraocular injections and even vitrectomy. Additionally, we provide laser treatment using the PASCAL Laser device, which is available only in some general hospitals, allowing for reduced pain and side effects during the treatment
-
Weekdays
08:30 a.m. - 05:30 p.m -
Saturdays
08:30 a.m. - 01:30 p.m -
Lunchtime
01:00 p.m. - 02:00 p.m
8F and 9F Sinsa Square, 652 Gangnam-daero, Gangnam-gu, Seoul
o straight for 5 minutes (330m) on foot from
Exit 6 of Sinsa Station on Subway Line 3
